LeR Advanced Sampling — Generating Detectable Events
This notebook is created by Phurailatpam Hemantakumar
This notebook demonstrates how to generate a specific number of detectable events and monitor detection rate convergence as a function of sample size using the LeR class.
Key Features: - Batch sampling until N detectable events are collected - Rate convergence monitoring with stopping criteria - Resume capability for interrupted sessions - Visualization of rate convergence and parameter distributions
Table of Contents
Initialize LeR
Sampling N Detectable Events
2.1 Unlensed Events
2.2 Rate Convergence (Unlensed)
2.3 Rate Stability (Unlensed)
2.4 Lensed Events
2.5 Rate Convergence (Lensed)
2.6 Rate Stability (Lensed)
2.7 Rate Comparison
Parameter Distributions: All vs Detectable
3.1 Unlensed Events
3.2 Lensed Events
Visualizing Lensed Detectable Events
4.1 Redshift Distribution
4.2 Magnification Ratio vs Time Delay
4.3 Caustic Plot
Summary
1. Initialize LeR
The LeR class is the main interface for simulating unlensed and lensed GW events and calculating detection rates. Default settings:
Event type: BBH (Binary Black Hole)
Lens model: EPL+Shear (Elliptical Power Law with external shear)
Detectors: H1, L1, V1 with O4 design sensitivity
Outputs are saved to ./ler_data by default.
[1]:
# Import LeR
from ler.rates import LeR
# Initialize LeR with default settings
# npool: number of parallel processes for sampling
ler = LeR(npool=6)
Initializing LeR class...
Initializing LensGalaxyParameterDistribution class...
Initializing OpticalDepth class
comoving_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/comoving_distance/comoving_distance_0.json
angular_diameter_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/angular_diameter_distance/angular_diameter_distance_0.json
angular_diameter_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/angular_diameter_distance/angular_diameter_distance_0.json
differential_comoving_volume interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/differential_comoving_volume/differential_comoving_volume_0.json
using ler available velocity dispersion function : velocity_dispersion_ewoud
velocity_dispersion_ewoud interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/velocity_dispersion/velocity_dispersion_ewoud_0.json
using ler available axis_ratio function : axis_ratio_rayleigh
axis_ratio_rayleigh interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/axis_ratio/axis_ratio_rayleigh_1.json
using ler available axis_rotation_angle function : axis_rotation_angle_uniform
using ler available density_profile_slope function : density_profile_slope_normal
using ler available external_shear function : external_shear_normal
Cross section interpolation data points loaded from ./interpolator_json/cross_section_function/cross_section_function_0.json
using ler available lens_redshift function : lens_redshift_strongly_lensed_numerical
Numerically solving the lens redshift distribution...
lens_redshift_strongly_lensed_numerical_epl_shear_galaxy interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/lens_redshift/lens_redshift_strongly_lensed_numerical_epl_shear_galaxy_1.json
lens_redshift_intrinsic interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/lens_redshift_intrinsic/lens_redshift_intrinsic_1.json
using ler available density_profile_slope_sl function : density_profile_slope_normal
using ler available external_shear_sl function : external_shear_normal
using ler available optical depth function : optical_depth_numerical
optical_depth_numerical interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/optical_depth/optical_depth_numerical_1.json
Initializing CBCSourceRedshiftDistribution class...
luminosity_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/luminosity_distance/luminosity_distance_0.json
differential_comoving_volume interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/differential_comoving_volume/differential_comoving_volume_0.json
using ler available merger rate density model: merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson_belczynski_ng
merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson_belczynski_ng interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson_belczynski_ng_0.json
merger_rate_density_detector_frame interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_detector_frame_1.json
source_redshift interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/source_redshift/source_redshift_0.json
Initializing CBCSourceParameterDistribution class...
using ler available zs function : source_redshift
using ler available source_frame_masses function : binary_masses_BBH_powerlaw_gaussian
using ler available geocent_time function : sampler_uniform
using ler available ra function : sampler_uniform
using ler available dec function : sampler_cosine
using ler available phase function : sampler_uniform
using ler available psi function : sampler_uniform
using ler available theta_jn function : sampler_sine
using ler available a_1 function : sampler_uniform
using ler available a_2 function : sampler_uniform
Faster, njitted and importance sampling based lens parameter sampler will be used.
Initializing GWSNR class...
psds not given. Choosing bilby's default psds
Interpolator will be loaded for L1 detector from ./interpolator_json/L1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for H1 detector from ./interpolator_json/H1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for V1 detector from ./interpolator_json/V1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Chosen GWSNR initialization parameters:
npool: 4
snr type: interpolation_aligned_spins
waveform approximant: IMRPhenomD
sampling frequency: 2048.0
minimum frequency (fmin): 20.0
reference frequency (f_ref): 20.0
mtot=mass1+mass2
min(mtot): 9.96
max(mtot) (with the given fmin=20.0): 500.0
detectors: ['L1', 'H1', 'V1']
psds: [[array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17d2bac50>], [array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17d25fba0>], [array([ 10. , 10.02306 , 10.046173, ...,
9954.0389 , 9976.993 , 10000. ], shape=(3000,)), array([1.22674387e-42, 1.20400299e-42, 1.18169466e-42, ...,
1.51304203e-43, 1.52010157e-43, 1.52719372e-43],
shape=(3000,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17cf21580>]]
#-------------------------------------
# LeR initialization input arguments:
#-------------------------------------
# LeR set up input arguments:
npool = 4,
z_min = 0.0,
z_max = 10.0,
event_type = 'BBH',
lens_type = 'epl_shear_galaxy',
cosmology = LambdaCDM(H0=70.0 km / (Mpc s), Om0=0.3, Ode0=0.7, Tcmb0=0.0 K, Neff=3.04, m_nu=None, Ob0=0.0),
pdet_finder = <bound method GWSNR.pdet of <gwsnr.core.gwsnr.GWSNR object at 0x17b778dc0>>,
json_file_names = dict(
ler_params = 'ler_params.json',
unlensed_param = 'unlensed_param.json',
unlensed_param_detectable = 'unlensed_param_detectable.json',
lensed_param = 'lensed_param.json',
lensed_param_detectable = 'lensed_param_detectable.json',
),
interpolator_directory = './interpolator_json',
ler_directory = './ler_data',
create_new_interpolator = dict(
merger_rate_density = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
redshift_distribution = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
luminosity_distance = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
differential_comoving_volume = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
source_frame_masses = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
geocent_time = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
ra = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
dec = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
phase = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
psi = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
theta_jn = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
a_1 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
a_2 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
tilt_1 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
tilt_2 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
phi_12 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
phi_jl = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
velocity_dispersion = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500, 'zl_resolution': 48},
axis_ratio = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500, 'sigma_resolution': 48},
lens_redshift = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 48, 'zl_resolution': 48},
lens_redshift_intrinsic = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
optical_depth = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 48},
comoving_distance = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
angular_diameter_distance = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
angular_diameter_distance_z1z2 = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 500},
density_profile_slope = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 100},
lens_parameters_kde_sl = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': 5000},
cross_section = {'create_new': False, 'resolution': [25, 25, 45, 15, 15]},
),
# LeR also takes other CBCSourceParameterDistribution class input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
source_priors = dict(
merger_rate_density = 'merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson_belczynski_ng',
zs = 'source_redshift',
source_frame_masses = 'binary_masses_BBH_powerlaw_gaussian',
geocent_time = 'sampler_uniform',
ra = 'sampler_uniform',
dec = 'sampler_cosine',
phase = 'sampler_uniform',
psi = 'sampler_uniform',
theta_jn = 'sampler_sine',
a_1 = 'sampler_uniform',
a_2 = 'sampler_uniform',
),
source_priors_params = dict(
merger_rate_density = {'R0': 1.9e-08, 'alpha_F': 2.57, 'beta_F': 5.83, 'c_F': 3.36},
zs = None,
source_frame_masses = {'mminbh': 4.98, 'mmaxbh': 112.5, 'alpha': 3.78, 'mu_g': 32.27, 'sigma_g': 3.88, 'lambda_peak': 0.03, 'delta_m': 4.8, 'beta': 0.81},
geocent_time = {'xmin': 1238166018, 'xmax': 1269702018},
ra = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
dec = None,
phase = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
psi = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 3.141592653589793},
theta_jn = None,
a_1 = {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8},
a_2 = {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8},
),
spin_zero = False,
spin_precession = False,
# LeR also takes other LensGalaxyParameterDistribution class input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
lens_functions = dict(
param_sampler_type = 'sample_all_routine_epl_shear_sl',
cross_section_based_sampler = 'importance_sampling_with_cross_section',
optical_depth = 'optical_depth_numerical',
cross_section = 'cross_section_epl_shear_interpolation',
),
lens_functions_params = dict(
param_sampler_type = None,
cross_section_based_sampler = {'n_prop': 200},
optical_depth = None,
cross_section = None,
),
lens_param_samplers = dict(
source_redshift_sl = 'strongly_lensed_source_redshifts',
lens_redshift = 'lens_redshift_strongly_lensed_numerical',
velocity_dispersion = 'velocity_dispersion_ewoud',
axis_ratio = 'axis_ratio_rayleigh',
axis_rotation_angle = 'axis_rotation_angle_uniform',
external_shear = 'external_shear_normal',
density_profile_slope = 'density_profile_slope_normal',
external_shear_sl = 'external_shear_normal',
density_profile_slope_sl = 'density_profile_slope_normal',
),
lens_param_samplers_params = dict(
source_redshift_sl = None,
lens_redshift = {'integration_size': 25000, 'use_multiprocessing': False},
velocity_dispersion = {'sigma_min': 100.0, 'sigma_max': 400.0, 'alpha': 0.94, 'beta': 1.85, 'phistar': np.float64(0.02099), 'sigmastar': 113.78, 'name': 'velocity_dispersion_ewoud'},
axis_ratio = {'q_min': 0.2, 'q_max': 1.0, 'name': 'axis_ratio_rayleigh'},
axis_rotation_angle = {'phi_min': 0.0, 'phi_max': 6.283185307179586, 'name': 'axis_rotation_angle_uniform'},
external_shear = {'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.05, 'name': 'external_shear_normal'},
density_profile_slope = {'mean': 1.99, 'std': 0.149, 'name': 'density_profile_slope_normal'},
external_shear_sl = {'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.05},
density_profile_slope_sl = {'mean': 2.078, 'std': 0.16},
),
# LeR also takes other ImageProperties class input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
n_min_images = 2,
n_max_images = 4,
time_window = 630720000,
lens_model_list = ['EPL_NUMBA', 'SHEAR'],
# LeR also takes other gwsnr.GWSNR input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
npool = 4,
snr_method = 'interpolation_aligned_spins',
snr_type = 'optimal_snr',
gwsnr_verbose = True,
multiprocessing_verbose = True,
pdet_kwargs = dict(
snr_th = 10.0,
snr_th_net = 10.0,
pdet_type = 'boolean',
distribution_type = 'noncentral_chi2',
include_optimal_snr = False,
include_observed_snr = False,
),
mtot_min = 9.96,
mtot_max = 500.0,
ratio_min = 0.1,
ratio_max = 1.0,
spin_max = 0.99,
mtot_resolution = 200,
ratio_resolution = 20,
spin_resolution = 10,
batch_size_interpolation = 1000000,
interpolator_dir = './interpolator_json',
create_new_interpolator = False,
sampling_frequency = 2048.0,
waveform_approximant = 'IMRPhenomD',
frequency_domain_source_model = 'lal_binary_black_hole',
minimum_frequency = 20.0,
reference_frequency = None,
duration_max = None,
duration_min = None,
fixed_duration = None,
mtot_cut = False,
psds = None,
ifos = None,
noise_realization = None,
ann_path_dict = None,
snr_recalculation = False,
snr_recalculation_range = [6, 14],
snr_recalculation_waveform_approximant = 'IMRPhenomXPHM',
psds_list = [[array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17d2bac50>], [array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17d25fba0>], [array([ 10. , 10.02306 , 10.046173, ...,
9954.0389 , 9976.993 , 10000. ], shape=(3000,)), array([1.22674387e-42, 1.20400299e-42, 1.18169466e-42, ...,
1.51304203e-43, 1.52010157e-43, 1.52719372e-43],
shape=(3000,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x17cf21580>]],
# To print all initialization input arguments, use:
ler._print_all_init_args()
2. Sampling N Detectable Events
Sample GW events until a specified number of detectable events is collected and stopping criteria are met.
Key features: - Batch processing: Events are sampled in batches for efficiency - Convergence monitoring: Rate stability is tracked via stopping criteria - Resume capability: Sampling can continue from previous sessions
2.1 Unlensed Events
Key parameters: - size: Target number of detectable events - batch_size: Events sampled per batch - stopping_criteria: Convergence conditions - pdet_threshold: Detection probability threshold - resume: Resume from previous session
[2]:
# Sample until we have at least 10,000 detectable unlensed events with converged rates
# use 'print(ler.selecting_n_unlensed_detectable_events.__doc__)' to see all input args
detectable_rate_unlensed, unlensed_param_detectable_n = ler.selecting_n_unlensed_detectable_events(
size=10000, # Target number of detectable events
batch_size=100000, # Events per batch
stopping_criteria=dict(
relative_diff_percentage=0.1, # Stop when rate change < 0.1%
number_of_last_batches_to_check=4 # Check last 4 batches for convergence
),
pdet_threshold=0.5, # Probability threshold for detection
resume=True, # Resume from previous state if available
output_jsonfile='unlensed_params_n_detectable.json', # Output file for detectable events
meta_data_file='meta_unlensed.json', # Store metadata (rates per batch)
pdet_type='boolean', # Detection type: 'boolean' or 'float'
trim_to_size=False, # Keep all events found until convergence
)
print(f"\n=== Unlensed N-Event Sampling Results ===")
print(f"Detectable event rate: {detectable_rate_unlensed:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Total detectable events collected: {len(unlensed_param_detectable_n['zs'])}")
stopping criteria set to when relative difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches is less than 0.1%.
sample collection will stop when the stopping criteria is met and number of detectable events exceeds the specified size.
Resuming from 11062.0 detectable events.
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.01807991 0.00109575 0.00877408 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.1% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
Given size=10000 reached
Stopping criteria met. There will be no more samples collected.
collected number of detectable events = 11062.0
stored detectable unlensed params in ./ler_data/unlensed_params_n_detectable.json
stored meta data in ./ler_data/meta_unlensed.json
=== Unlensed N-Event Sampling Results ===
Detectable event rate: 2.8946e+02 events per year
Total detectable events collected: 11062
2.2 Rate Convergence (Unlensed)
Visualize how detection rate evolves with sample size. A converged rate indicates stable statistics.
[3]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
# Load metadata containing rates for each batch
meta_data = get_param_from_json(ler.ler_directory + '/meta_unlensed.json')
# Plot rate vs sampling size
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.plot(
meta_data['events_total'],
meta_data['total_rate'],
'o-',
linewidth=2,
markersize=6,
color='C0',
label='Detectable rate'
)
plt.xlabel('Total Number of Events Sampled', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Detectable Event Rate (per year)', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Unlensed Rate Convergence Across Batches', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend(fontsize=11)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
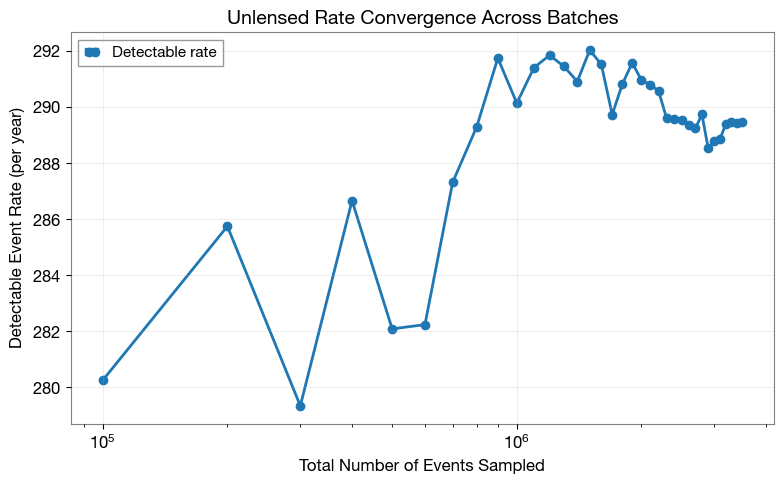
2.3 Rate Stability (Unlensed)
Quantify convergence using mean and standard deviation from the last few batches.
[4]:
import numpy as np
# Select rates from the last 4 batches
idx_converged = [-4, -3, -2, -1]
rates_converged = np.array(meta_data['total_rate'])[idx_converged]
if len(rates_converged) > 0:
mean_rate = rates_converged.mean()
std_rate = rates_converged.std()
print(f"=== Unlensed Rate Stability Analysis ===")
print(f"Number of batches analyzed: {len(rates_converged)}")
print(f"Mean rate: {mean_rate:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Standard deviation: {std_rate:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Relative uncertainty: {(std_rate/mean_rate)*100:.3f}%")
else:
print("Not enough batches to assess convergence.")
# Update the rate with the converged mean
detectable_rate_unlensed = mean_rate
=== Unlensed Rate Stability Analysis ===
Number of batches analyzed: 4
Mean rate: 2.8944e+02 events/year
Standard deviation: 2.2384e-02 events/year
Relative uncertainty: 0.008%
2.4 Lensed Events
Generate lensed detectable events. For lensed events, we can specify: - pdet_threshold: List of detection thresholds for each image - num_img: Number of images that must meet each corresponding threshold
Here, stopping_criteria=None with size=1000 means sampling continues until at least 1000 detectable lensed events are collected.
[5]:
# Sample until we have at least 1,000 detectable lensed events
# use 'print(ler.selecting_n_lensed_detectable_events.__doc__)' to see all input args
detectable_rate_lensed, lensed_param_detectable_n = ler.selecting_n_lensed_detectable_events(
size=1000, # Target number of detectable events
batch_size=50000, # Events per batch
stopping_criteria=None, # No stopping criteria (sample until size is reached)
pdet_threshold=[0.5, 0.5], # Detection thresholds for images
num_img=[1, 1], # Number of images required per threshold
resume=True, # Resume from previous state if available
output_jsonfile='lensed_params_n_detectable.json',
meta_data_file='meta_lensed.json',
pdet_type='boolean',
trim_to_size=False,
)
print(f"\n=== Lensed N-Event Sampling Results ===")
print(f"Detectable event rate: {detectable_rate_lensed:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Total detectable events collected: {len(lensed_param_detectable_n['zs'])}")
stopping criteria not set. sample collection will stop when number of detectable events exceeds the specified size.
Resuming from 1014.0 detectable events.
Given size=1000 reached
Stopping criteria met. There will be no more samples collected.
collected number of detectable events = 1014.0
storing detectable lensed params in ./ler_data/lensed_params_n_detectable.json
storing meta data in ./ler_data/meta_lensed.json
=== Lensed N-Event Sampling Results ===
Detectable event rate: 9.5750e-02 events per year
Total detectable events collected: 1014
2.5 Rate Convergence (Lensed)
Visualize the lensed detection rate evolution across batches.
[6]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
# Load metadata containing rates for each batch
meta_data = get_param_from_json(ler.ler_directory + '/meta_lensed.json')
# Plot rate vs sampling size
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.plot(
meta_data['events_total'],
meta_data['total_rate'],
'o-',
linewidth=2,
markersize=6,
color='C1',
label='Detectable rate'
)
plt.xlabel('Total Number of Events Sampled', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Detectable Event Rate (per year)', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Lensed Rate Convergence Across Batches', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend(fontsize=11)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
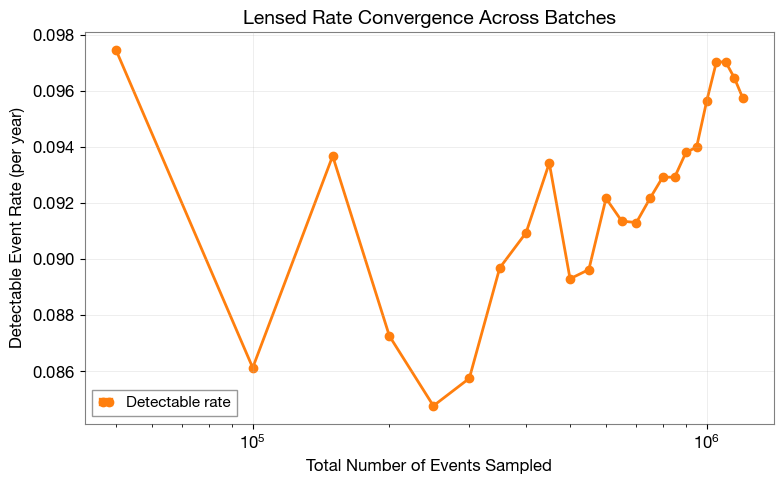
2.6 Rate Stability (Lensed)
Quantify convergence using mean and standard deviation from the last few batches.
[7]:
import numpy as np
# Select rates from the last 4 batches
idx_converged = [-4, -3, -2, -1]
rates_converged = np.array(meta_data['total_rate'])[idx_converged]
if len(rates_converged) > 0:
mean_rate = rates_converged.mean()
std_rate = rates_converged.std()
print(f"=== Lensed Rate Stability Analysis ===")
print(f"Number of batches analyzed: {len(rates_converged)}")
print(f"Mean rate: {mean_rate:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Standard deviation: {std_rate:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Relative uncertainty: {(std_rate/mean_rate)*100:.3f}%")
else:
print("Not enough batches to assess convergence.")
# Update the rate with the converged mean
detectable_rate_lensed = mean_rate
=== Lensed Rate Stability Analysis ===
Number of batches analyzed: 4
Mean rate: 9.6567e-02 events/year
Standard deviation: 5.2511e-04 events/year
Relative uncertainty: 0.544%
2.7 Rate Comparison
Compare detection rates between lensed and unlensed events.
[8]:
# Compare lensed vs unlensed rates
print(f"=== Detection Rate Comparison ===")
print(f"Unlensed detectable rate: {detectable_rate_unlensed:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Lensed detectable rate: {detectable_rate_lensed:.4e} events/year")
print(f"Ratio (Unlensed/Lensed): {(detectable_rate_unlensed/detectable_rate_lensed):.2f}")
=== Detection Rate Comparison ===
Unlensed detectable rate: 2.8944e+02 events/year
Lensed detectable rate: 9.6567e-02 events/year
Ratio (Unlensed/Lensed): 2997.28
3. Parameter Distributions: All vs Detectable
Compare parameter distributions between all sampled events and detectable events. Corner plots reveal selection effects introduced by detector sensitivity.
3.1 Unlensed Events
Generate a large sample of all unlensed events (both detectable and non-detectable) for comparison.
[9]:
# Generate a large sample of all unlensed events for comparison
unlensed_param = ler.unlensed_cbc_statistics(size=50000, resume=True, output_jsonfile='unlensed_params_all.json')
print(f"Total unlensed events sampled: {len(unlensed_param['zs'])}")
unlensed params will be stored in ./ler_data/unlensed_params_all.json
removing ./ler_data/unlensed_params_all.json if it exists
resuming from ./ler_data/unlensed_params_all.json
Batch no. 1
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
unlensed parameters already sampled.
saving all unlensed parameters in ./ler_data/unlensed_params_all.json
Total unlensed events sampled: 50000
Corner plot comparing all sampled events vs detectable events:
[17]:
import corner
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
# Load data
param = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/unlensed_params_all.json')
param_detectable = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/unlensed_params_n_detectable.json')
# Parameters to compare
param_names = ['zs', 'ra', 'dec', 'theta_jn', 'mass_1_source', 'mass_2_source']
labels = ['$z_s$', 'RA', 'Dec', r'$\theta_{JN}$', '$m_1$ [$M_\odot$]', '$m_2$ [$M_\odot$]']
# Prepare data for corner plot
samples_all = np.stack([param[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
samples_detectable = np.stack([param_detectable[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
# Create corner plot for all events
fig = corner.corner(
samples_all,
labels=labels,
color='C0',
alpha=0.5,
plot_density=False,
plot_datapoints=False,
smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
# Overlay detectable events
corner.corner(
samples_detectable,
labels=labels,
color='C1',
alpha=0.5,
fig=fig,
plot_density=False,
plot_datapoints=False,
smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
# Add legend
blue_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C0', label='All events')
orange_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C1', label='Detectable only')
fig.legend(handles=[blue_line, orange_line], loc='upper right',
bbox_to_anchor=(0.95, 0.95), fontsize=14)
fig.suptitle('Unlensed Events: All vs Detectable', fontsize=16, y=1.02)
plt.show()
WARNING:root:Too few points to create valid contours
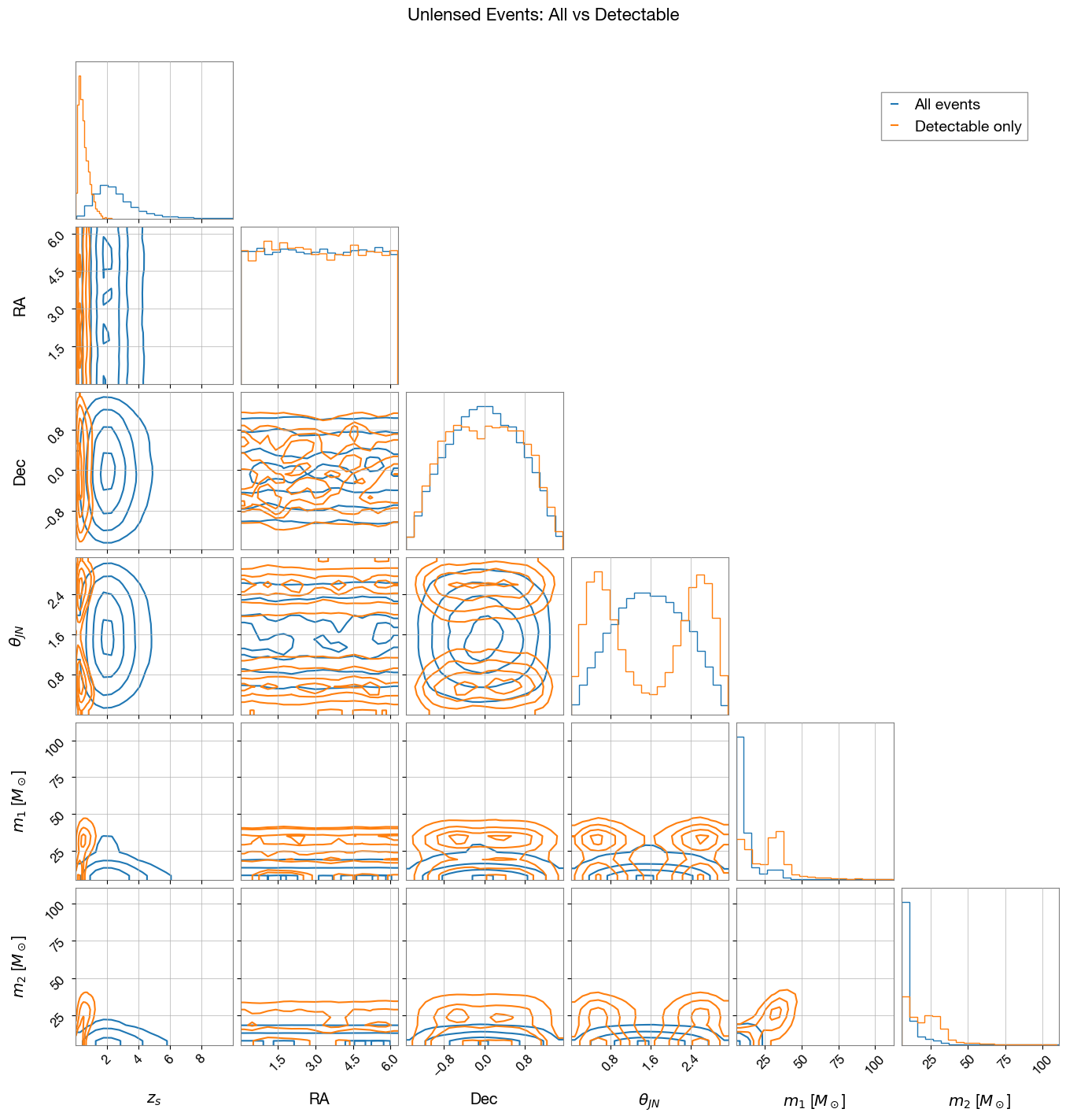
3.2 Lensed Events
Compare intrinsic, strongly lensed, and detectable lensed event distributions. First, generate strongly lensed events:
[11]:
# Generate a large sample of all lensed events for comparison
lensed_param = ler.lensed_cbc_statistics(size=50000, resume=True, output_jsonfile='lensed_params_all.json')
print(f"Total lensed events sampled: {len(lensed_param['zs'])}")
lensed params will be stored in ./ler_data/lensed_params_all.json
removing ./ler_data/lensed_params_all.json if it exists
resuming from ./ler_data/lensed_params_all.json
Batch no. 1
sampling lensed params...
sampling lens parameters with sample_all_routine_epl_shear_sl...
solving lens equations...
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 50000/50000 [00:11<00:00, 4235.41it/s]
calculating pdet...
lensed parameters already sampled.
saving all lensed parameters in ./ler_data/lensed_params_all.json
Total lensed events sampled: 50000
Generate intrinsic parameters (without strong lensing selection):
[26]:
# Generate a large sample of all lensed events for comparison
lensed_param_intrinsic = ler.sample_all_routine_epl_shear_intrinsic(size=50000)
print(f"Total lensed events sampled: {len(lensed_param_intrinsic['zs'])}")
# save to file
from ler.utils import append_json
append_json(ler.ler_directory+'/lensed_param_intrinsic.json', lensed_param_intrinsic, replace=True);
Total lensed events sampled: 50000
Corner plot comparing intrinsic, strongly lensed, and detectable events:
[28]:
import corner
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
# Load data
param = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_params_all.json')
param_detectable = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_params_n_detectable.json')
param_intrinsic = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_param_intrinsic.json')
# lensed_param_intrinsic is already in memory from cell 24
# Lensing-specific parameters to compare
param_names = ['zs', 'zl', 'sigma', 'q', 'gamma', 'gamma1', 'gamma2']
labels = ['$z_s$', '$z_l$', r'$\sigma$ [km/s]', '$q$', r'$\gamma$', r'$\gamma_1$', r'$\gamma_2$']
# Prepare data for corner plot
samples_intrinsic = np.stack([param_intrinsic[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
samples_all = np.stack([param[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
samples_detectable = np.stack([param_detectable[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
# Create corner plot for intrinsic events
fig = corner.corner(
samples_intrinsic,
labels=labels,
color='C2',
alpha=0.5,
plot_density=False,
plot_datapoints=False,
smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
# Overlay strongly lensed events
corner.corner(
samples_all,
labels=labels,
color='C0',
alpha=0.5,
fig=fig,
plot_density=False,
plot_datapoints=False,
smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
# Overlay detectable events
corner.corner(
samples_detectable,
labels=labels,
color='C1',
alpha=0.5,
fig=fig,
plot_density=False,
plot_datapoints=False,
smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
# Add legend
green_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C2', label='Intrinsic')
blue_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C0', label='Strongly lensed')
orange_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C1', label='Detectable only')
fig.legend(handles=[green_line, blue_line, orange_line], loc='upper right',
bbox_to_anchor=(0.95, 0.95), fontsize=14)
fig.suptitle('Lensed Events: Intrinsic vs. Strongly Lensed vs. Detectable', fontsize=16, y=1.02)
plt.show()
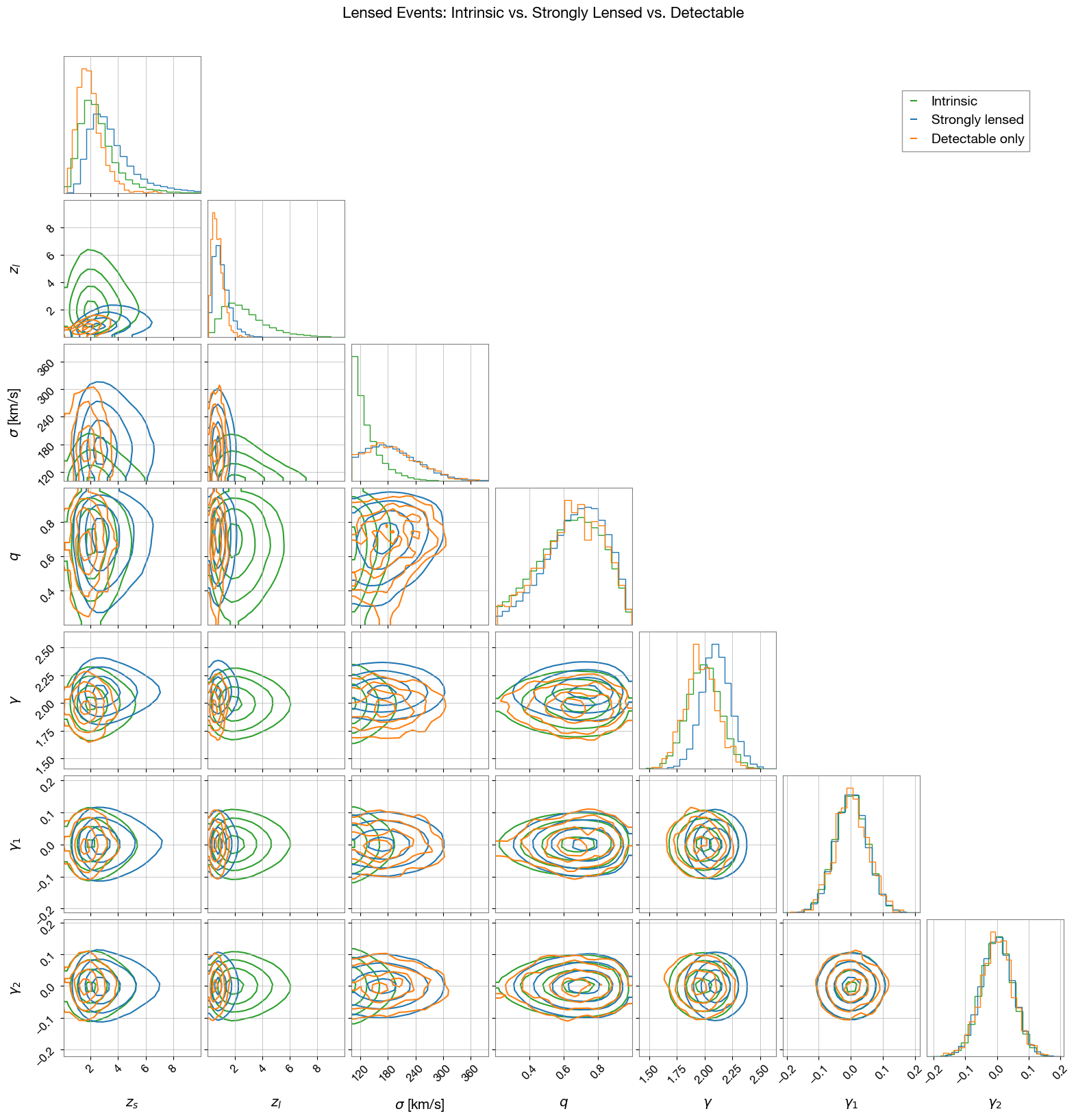
4. Visualizing Lensed Detectable Events
Visualize properties of detectable lensed events. An example event is highlighted in each plot to show individual characteristics within the population.
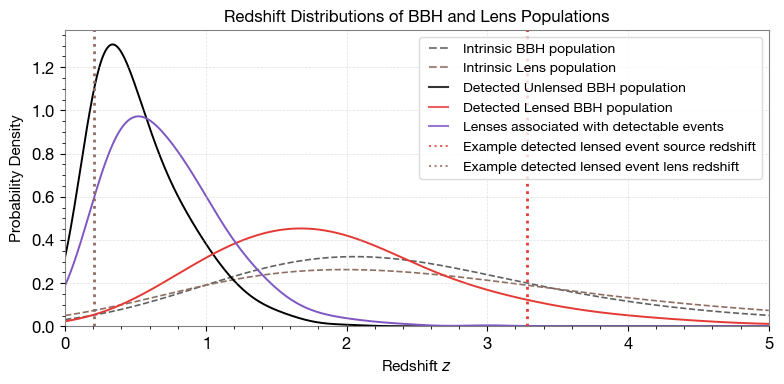
4.1 Redshift Distribution
Compare redshift distributions of intrinsic and detected populations.
[29]:
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import AutoMinorLocator
np.random.seed(100)
# Load data
unlensed_params_det = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/unlensed_params_n_detectable.json')
lensed_params_det = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_params_n_detectable.json')
unlensed_params = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/unlensed_param.json')
lensed_params = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_param.json')
lensed_params_intrinsic = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/lensed_param_intrinsic.json')
bbh_pop_intrinsic = unlensed_params['zs']
unlensed_bbh_pop_detected = unlensed_params_det['zs']
lensed_bbh_pop_detected = lensed_params_det['zs']
lens_detected = lensed_params_det['zl']
lens_dist_intrinsic = lensed_params_intrinsic['zl']
# create gaussian kde
from scipy.stats import gaussian_kde
bandwidth = 0.4
kde_bbh_pop_intrinsic = gaussian_kde(bbh_pop_intrinsic, bw_method=bandwidth)
kde_unlensed_bbh_pop_detected = gaussian_kde(unlensed_bbh_pop_detected, bw_method=bandwidth)
kde_lensed_bbh_pop_detected = gaussian_kde(lensed_bbh_pop_detected, bw_method=bandwidth)
kde_lens_dist_intrinsic = gaussian_kde(lens_dist_intrinsic, bw_method=bandwidth)
kde_lens_detected = gaussian_kde(lens_detected, bw_method=bandwidth)
# Choose a random detected lensed event to highlight
pdet = lensed_params_det['pdet_net']
idx_4img = pdet > 0.5
idx_4img = np.sum(idx_4img, axis=1) ==2 # 2 images detected
chosen_idx_list = np.where(idx_4img)[0]
chosen_idx = chosen_idx_list[10] # pick the 10th one for consistency
print(f"Chosen detected lensed event index: {chosen_idx}")
# ---------- Data ----------
z = np.linspace(0, 5, 1000)
# ---------- Plot ----------
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
colors = {
"black": "#000000",
"violet": "#7E57C2",
"brown": "#8D6E63",
"grey": "#616161",
"red": "#E53935",
"blue": "#1E88E5",
}
# intrinsic distributions
ax.plot(z, kde_bbh_pop_intrinsic(z), label='Intrinsic BBH population',
color=colors["grey"], linestyle='--', linewidth=1.2)
ax.plot(z, kde_lens_dist_intrinsic(z), label='Intrinsic Lens population',
color=colors["brown"], linestyle='--', linewidth=1.2)
# detected distributions
ax.plot(z, kde_unlensed_bbh_pop_detected(z), label='Detected Unlensed BBH population',
color=colors["black"], linestyle='-', linewidth=1.4)
ax.plot(z, kde_lensed_bbh_pop_detected(z), label='Detected Lensed BBH population',
color=colors["red"], linestyle='-', linewidth=1.4)
ax.plot(z, kde_lens_detected(z), label='Lenses associated with detectable events',
color=colors["violet"], linestyle='-', linewidth=1.4)
# Example detected lensed event redshifts
ax.axvline(lensed_params_det['zs'][chosen_idx],
color=colors["red"], linestyle=':', linewidth=2,
label='Example detected lensed event source redshift')
ax.axvline(lensed_params_det['zl'][chosen_idx],
color=colors["brown"], linestyle=':', linewidth=2,
label='Example detected lensed event lens redshift')
# ---------- Legend ----------
legend = ax.legend(
handlelength=2.0,
loc='upper right',
bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1),
frameon=True,
fontsize=10.,
edgecolor='lightgray'
)
legend.get_frame().set_boxstyle('Round', pad=0.0, rounding_size=0.2)
for handle in legend.get_lines():
handle.set_linewidth(1.5)
handle.set_alpha(0.8)
# ---------- Axes labels, limits, and grid ----------
ax.set_xlabel(r'Redshift $z$', fontsize=11)
ax.set_ylabel(r'Probability Density', fontsize=11)
ax.set_xlim(0, 5)
ax.set_ylim(0, None)
ax.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
# add title
ax.set_title('Redshift Distributions of BBH and Lens Populations', fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('lens_paramters_baseline_redshift_distributions.svg',
# dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight', transparent=True)
plt.show()
Chosen detected lensed event index: 10
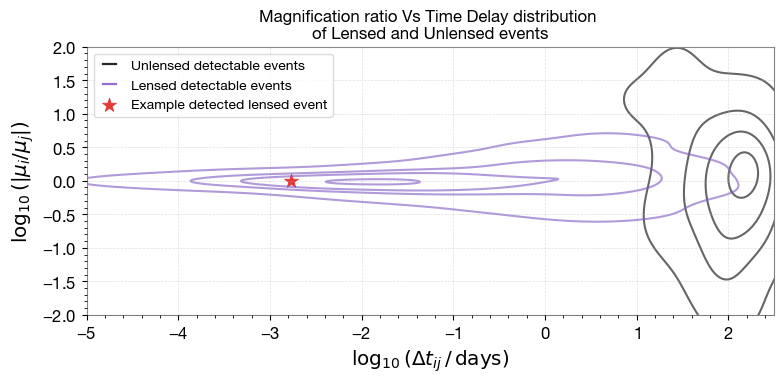
4.2 Magnification Ratio vs Time Delay
Relative magnification vs time delay distinguishes lensed from unlensed events.
[30]:
from ler.utils import relative_mu_dt_unlensed, relative_mu_dt_lensed, mu_vs_dt_plot
# for unlensed detectable events
dmu_unlensed, dt_unlensed = relative_mu_dt_unlensed(param=unlensed_params_det)
# for lensed detectable events
lensed_dict = relative_mu_dt_lensed(lensed_param=lensed_params_det)
dt_lensed = np.concatenate((lensed_dict['dt_rel0'], lensed_dict['dt_rel90']))
dmu_lensed = np.concatenate((lensed_dict['mu_rel0'], lensed_dict['mu_rel90']))
# chosen example index for 4 images, find time delays and magnifications
chosen_lens_dt = lensed_params_det['time_delays'][chosen_idx]
chosen_lens_mu = lensed_params_det['magnifications'][chosen_idx]
pdet = lensed_params_det['pdet_net'][chosen_idx]
dt_lensed_chosen = np.log10((chosen_lens_dt[2]-chosen_lens_dt[1])/ (60 * 60 * 24))
dmu_lensed_chosen = np.log10(abs(chosen_lens_mu[2]/chosen_lens_mu[1]))
# ---------------------------------------
# Plot Magnification ratio Vs Time Delay
# ---------------------------------------
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
colors = {
"black": "#000000",
"violet": "#7E57C2",
"brown": "#8D6E63",
"grey": "#616161",
"red": "#E53935",
"blue": "#1E88E5",
}
# Use your existing helper without modification
mu_vs_dt_plot(dt_unlensed, dmu_unlensed, colors=[colors['black']]*5)
mu_vs_dt_plot(dt_lensed, dmu_lensed, colors=[colors['violet']]*5)
# Proxy artists for legend
# Proxy artists for legend
ax.plot([], [], color=colors['black'], linestyle='-', label='Unlensed detectable events', linewidth=1.5)
ax.plot([], [], color=colors['violet'], linestyle='-', label='Lensed detectable events', linewidth=1.5)
# Chosen example point
ax.scatter(
dt_lensed_chosen, dmu_lensed_chosen,
color=colors['red'], marker='*', s=110, linewidths=0.6,
label='Example detected lensed event'
)
# ---------- Legend ----------
legend = ax.legend(
handlelength=1.5,
loc='upper left',
bbox_to_anchor=(0, 1),
frameon=True,
fontsize=10,
edgecolor='lightgray'
)
legend.get_frame().set_boxstyle('Round', pad=0.0, rounding_size=0.2)
for handle in legend.get_lines():
handle.set_linewidth(1.6)
handle.set_alpha(0.85)
# add title
ax.set_title('Magnification ratio Vs Time Delay distribution \nof Lensed and Unlensed events', fontsize=12)
# ---------- Axes, ticks, grid ----------
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\log_{10}(\Delta t_{ij} \,/\, \mathrm{days})$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$\log_{10}(|\mu_i / \mu_j|)$')
ax.set_xlim(-5, 2.5)
ax.set_ylim(-2, 2)
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
ax.grid(alpha=0.38, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('mu_vs_dt_science_ieee.svg', dpi=600, bbox_inches='tight', transparent=True)
plt.show()
# time: 32s
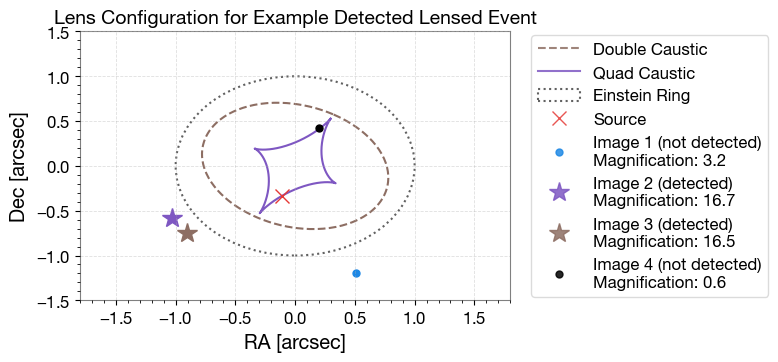
4.3 Caustic Plot
Lens configuration for an example event, showing caustics, critical curves, and image positions.
[31]:
from lenstronomy.LensModel.lens_model import LensModel
from lenstronomy.LensModel.Solver.lens_equation_solver import LensEquationSolver
from lenstronomy.LensModel.Solver.epl_shear_solver import caustics_epl_shear
# import phi_q2_ellipticity
from lenstronomy.Util.param_util import phi_q2_ellipticity
# ---------- Custom color palette ----------
colors = {
"black": "#000000",
"violet": "#7E57C2",
"brown": "#8D6E63",
"grey": "#616161",
"red": "#E53935",
"blue": "#1E88E5",
"green": "#43A047",
"orange": "#FB8C00",
}
# ----- Lens setup -----
lens_model_list = ["EPL", "SHEAR"]
lensModel = LensModel(lens_model_list=lens_model_list)
lens_eq_solver = LensEquationSolver(lensModel)
q = lensed_params_det['q'][chosen_idx]
phi = lensed_params_det['phi'][chosen_idx]
e1, e2 = phi_q2_ellipticity(phi, q)
kwargs_spep = {
'theta_E': 1.0,
'e1': e1,
'e2': e2,
'gamma': lensed_params_det['gamma'][chosen_idx],
'center_x': 0.0,
'center_y': 0.0,
}
kwargs_shear = {
'gamma1': lensed_params_det['gamma1'][chosen_idx],
'gamma2': lensed_params_det['gamma2'][chosen_idx]
}
kwargs_lens = [kwargs_spep, kwargs_shear]
# ----- Solve image configuration -----
theta_E = lensed_params_det['theta_E'][chosen_idx]
# unscaled source position
beta_ra = lensed_params_det['x_source'][chosen_idx]/theta_E
beta_dec = lensed_params_det['y_source'][chosen_idx]/theta_E
theta_ra, theta_dec = lens_eq_solver.image_position_from_source(
sourcePos_x=beta_ra, sourcePos_y=beta_dec, kwargs_lens=kwargs_lens,
solver="analytical", magnification_limit=1.0/100.0, arrival_time_sort=True
)
magnifications = lensModel.magnification(theta_ra, theta_dec, kwargs_lens)
magnifications = np.abs(np.array(magnifications))
# print(f"Magnifications calculated: {magnifications}")
# ----- Figure -----
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6)) # wider figure
# Caustics
cp = caustics_epl_shear(kwargs_lens, return_which="double", maginf=-100)
ax.plot(cp[0], cp[1], color=colors['brown'], linewidth=1.5, linestyle='--', label='Double Caustic')
cp = caustics_epl_shear(kwargs_lens, return_which="quad", maginf=-100)
ax.plot(cp[0], cp[1], color=colors['violet'], linewidth=1.5, linestyle='-', label='Quad Caustic')
# Einstein ring
theta_E = 1.0
circle = plt.Circle((0, 0), theta_E, color=colors['grey'], fill=False,
linestyle='dotted', linewidth=1.5, label='Einstein Ring')
ax.add_artist(circle)
# Source position
ax.plot(beta_ra, beta_dec, marker='x', ls='None', color=colors['red'], label='Source', markersize=10)
# Image positions
img_colors = [colors['blue'], colors['violet'], colors['brown'], colors['black']]
pdet_image = lensed_params_det['pdet_net'][chosen_idx]
for i in range(len(theta_ra)):
if pdet_image[i] >= 0.5:
ax.plot(theta_ra[i], theta_dec[i], marker='*', ls='None',
color=img_colors[i % len(img_colors)],
label=f'Image {i+1} (detected)\nMagnification: {magnifications[i]:.1f}', markersize=15)
else:
ax.plot(theta_ra[i], theta_dec[i], marker='.', ls='None',
color=img_colors[i % len(img_colors)],
label=f'Image {i+1} (not detected)\nMagnification: {magnifications[i]:.1f}', markersize=10)
# Axes & Grid
ax.set_xlabel('RA [arcsec]')
ax.set_ylabel('Dec [arcsec]')
dim_x, dim_y = 1.8, 1.5 # rectangular window
ax.set_xlim(-dim_x, dim_x)
ax.set_ylim(-dim_y, dim_y)
# Relax the aspect ratio → visually rectangular (with adjustable='box' to respect figure size)
ax.set_aspect(6/8, adjustable='box')
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator())
ax.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.6)
# Legend on the side
legend = ax.legend(
handlelength=2.5,
loc='center left',
bbox_to_anchor=(1.03, 0.5),
frameon=True,
fontsize=12,
edgecolor='lightgray',
numpoints=1, # Show only one marker per legend entry
scatterpoints=1
)
legend.get_frame().set_boxstyle('Round', pad=0.0, rounding_size=0.2)
for handle in legend.get_lines():
handle.set_linewidth(1.5)
handle.set_alpha(0.85)
# add title
ax.set_title('Lens Configuration for Example Detected Lensed Event', fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig('lens_configuration_rectangular.svg', dpi=600, bbox_inches='tight', transparent=True)
plt.show()
5. Summary
This notebook demonstrated advanced sampling capabilities of LeR for generating detectable GW events.
Key Takeaways:
N-Event Sampling:
selecting_n_unlensed_detectable_eventsandselecting_n_lensed_detectable_eventscollect a target number of detectable events with convergence monitoring.Rate Convergence: Tracking rates across batches verifies statistical stability.
Resume Capability: Sampling can be interrupted and resumed without losing progress.
Selection Effects: The corner plots reveal how detector sensitivity and strong lensing selection bias the observed populations:
Detector sensitivity effects:
Lower redshift events are preferentially detected
Higher mass events have higher detection probability
Sky location and orientation effects are visible
Strong lensing selection effects:
Higher magnification events are more likely to be detected
Lensed events tend to occur at higher redshifts
Lens velocity dispersion influences strong lensing due to increased lensing cross-section
Lens galaxy density profile slope affects detectability
Lensing Visualization: The redshift distributions, magnification-time delay plots, and caustic diagrams provide insight into the properties of detectable lensed events.
