GWRATES complete example
This notebook is created by Phurailatpam Hemantakumar.
GWRATES is a comprehensive framework for simulating gravitational wave (GW) events and calculating their detection rates. This notebook provides a complete example of CBC event simulation and rate calculation.
Table of Contents
Part 1: Basic GW Event Simulation and Rate Calculation (BBH Example)
1.1 Initialize GWRATES
1.2 Simulate GW Population
1.3 Calculate Detection Rates
1.4 Inspect Generated Parameters
1.5 Access Saved Data Files
1.6 Load and Examine Saved Parameters
1.7 Examine Available Prior Functions
1.8 Visualize Parameter Distributions
Part 2: Custom Functions and Parameters
2.1 Define Custom Source Frame Masses
2.2 Define Event Type with Non-Spinning Configuration
2.3 Define Custom Merger Rate Density
2.4 Define Custom Detection Criteria
2.5 Initialize GWRATES with Custom Settings
2.6 Sample GW Parameters with Custom Settings
2.7 Calculate Rates with Custom Settings
2.8 Compare Default and Custom Mass Distributions
Part 3: Advanced Sampling - Generating Detectable Events
3.1 Initialize GWRATES for N-Event Sampling
3.2 Sample Until N Detectable Events Are Found
3.3 Analyze Rate Convergence
3.4 Assess Rate Stability
3.5 Overlapping plot between the all sampled and detectable event parameters
Part 1: Basic GW Event Simulation and Rate Calculation (BBH Example)
This section demonstrates a quick example to simulate binary black hole mergers and calculate their detection rates.
1.1 Initialize GWRATES
The GWRATES class is the main interface for simulating GW events and calculating rates. By default, it uses: - Event type: BBH (Binary Black Hole) - Detectors: H1, L1, V1 (LIGO Hanford, LIGO Livingston, Virgo) with O4 design sensitivity
All outputs will be saved in the ./ler_data directory.
[33]:
# Import the GWRATES class from the ler package
from ler.rates import GWRATES
# Initialize GWRATES with default settings
ler = GWRATES(verbose=True)
Initializing GWRATES class...
Initializing CBCSourceRedshiftDistribution...
luminosity_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/luminosity_distance/luminosity_distance_0.json
differential_comoving_volume interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/differential_comoving_volume/differential_comoving_volume_0.json
using ler available merger rate density model: merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018
merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018 interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018_0.json
merger_rate_density_detector_frame interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_detector_frame_1.json
source_redshift interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/source_redshift/source_redshift_0.json
Initializing CBCSourceParameterDistribution...
using ler available zs function : source_redshift
using ler available source_frame_masses function : binary_masses_BBH_popI_II_powerlaw_gaussian
using ler available geocent_time function : sampler_uniform
using ler available ra function : sampler_uniform
using ler available dec function : sampler_cosine
using ler available phase function : sampler_uniform
using ler available psi function : sampler_uniform
using ler available theta_jn function : sampler_sine
using ler available a_1 function : sampler_uniform
using ler available a_2 function : sampler_uniform
Initializing GWSNR class...
psds not given. Choosing bilby's default psds
Interpolator will be loaded for L1 detector from ./interpolator_json/L1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for H1 detector from ./interpolator_json/H1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for V1 detector from ./interpolator_json/V1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Chosen GWSNR initialization parameters:
npool: 4
snr type: interpolation_aligned_spins
waveform approximant: IMRPhenomD
sampling frequency: 2048.0
minimum frequency (fmin): 20.0
reference frequency (f_ref): 20.0
mtot=mass1+mass2
min(mtot): 9.96
max(mtot) (with the given fmin=20.0): 500.0
detectors: ['L1', 'H1', 'V1']
psds: [[array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x3296f6de0>], [array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x327cfaac0>], [array([ 10. , 10.02306 , 10.046173, ...,
9954.0389 , 9976.993 , 10000. ], shape=(3000,)), array([1.22674387e-42, 1.20400299e-42, 1.18169466e-42, ...,
1.51304203e-43, 1.52010157e-43, 1.52719372e-43],
shape=(3000,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x32a4863e0>]]
#----------------------------------------
# GWRATES initialization input arguments:
#----------------------------------------
# GWRATES set up input arguments:
npool = 4,
z_min = 0.0,
z_max = 10.0,
event_type = 'BBH',
cosmology = LambdaCDM(H0=70.0 km / (Mpc s), Om0=0.3, Ode0=0.7, Tcmb0=0.0 K, Neff=3.04, m_nu=None, Ob0=None),
pdet_finder = <bound method GWSNR.pdet of <gwsnr.core.gwsnr.GWSNR object at 0x327c27e50>>,
json_file_names = dict(
gwrates_params = 'gwrates_params.json',
gw_param = 'gw_param.json',
gw_param_detectable = 'gw_param_detectable.json',
),
interpolator_directory = './interpolator_json',
ler_directory = './ler_data',
# GWRATES also takes other CBCSourceParameterDistribution class input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
source_priors = dict(
merger_rate_density = 'merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018',
zs = 'source_redshift',
source_frame_masses = 'binary_masses_BBH_popI_II_powerlaw_gaussian',
geocent_time = 'sampler_uniform',
ra = 'sampler_uniform',
dec = 'sampler_cosine',
phase = 'sampler_uniform',
psi = 'sampler_uniform',
theta_jn = 'sampler_sine',
a_1 = 'sampler_uniform',
a_2 = 'sampler_uniform',
),
source_priors_params = dict(
merger_rate_density = {'R0': 2.39e-08, 'b2': 1.6, 'b3': 2.1, 'b4': 30},
zs = None,
source_frame_masses = {'mminbh': 4.98, 'mmaxbh': 112.5, 'alpha': 3.78, 'mu_g': 32.27, 'sigma_g': 3.88, 'lambda_peak': 0.03, 'delta_m': 4.8, 'beta': 0.81},
geocent_time = {'xmin': 1238166018, 'xmax': 1269702018},
ra = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
dec = None,
phase = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
psi = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 3.141592653589793},
theta_jn = None,
a_1 = {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8},
a_2 = {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8},
),
spin_zero = False,
spin_precession = False,
# GWRATES also takes other gwsnr.GWSNR input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
npool = 4,
snr_method = 'interpolation_aligned_spins',
snr_type = 'optimal_snr',
gwsnr_verbose = True,
multiprocessing_verbose = True,
pdet_kwargs = dict(
snr_th = 10.0,
snr_th_net = 10.0,
pdet_type = 'boolean',
distribution_type = 'noncentral_chi2',
include_optimal_snr = False,
include_observed_snr = False,
),
mtot_min = 9.96,
mtot_max = 500.0,
ratio_min = 0.1,
ratio_max = 1.0,
spin_max = 0.99,
mtot_resolution = 200,
ratio_resolution = 20,
spin_resolution = 10,
batch_size_interpolation = 1000000,
interpolator_dir = './interpolator_json',
create_new_interpolator = False,
sampling_frequency = 2048.0,
waveform_approximant = 'IMRPhenomD',
frequency_domain_source_model = 'lal_binary_black_hole',
minimum_frequency = 20.0,
reference_frequency = None,
duration_max = None,
duration_min = None,
fixed_duration = None,
mtot_cut = False,
psds = None,
ifos = None,
noise_realization = None,
ann_path_dict = None,
snr_recalculation = False,
snr_recalculation_range = [6, 14],
snr_recalculation_waveform_approximant = 'IMRPhenomXPHM',
psds_list = [[array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x3296f6de0>], [array([ 10.21659, 10.23975, 10.26296, ..., 4972.81 ,
4984.081 , 4995.378 ], shape=(2736,)), array([4.43925574e-41, 4.22777986e-41, 4.02102594e-41, ...,
6.51153524e-46, 6.43165104e-46, 6.55252996e-46],
shape=(2736,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x327cfaac0>], [array([ 10. , 10.02306 , 10.046173, ...,
9954.0389 , 9976.993 , 10000. ], shape=(3000,)), array([1.22674387e-42, 1.20400299e-42, 1.18169466e-42, ...,
1.51304203e-43, 1.52010157e-43, 1.52719372e-43],
shape=(3000,)), <scipy.interpolate._interpolate.interp1d object at 0x32a4863e0>]],
To print all initialization input arguments, use:
ler._print_all_init_args()
1.2 Simulate GW Population
Generate a population of Compact Binary Coalescence (CBC) events. This step: - Samples intrinsic (masses and spins) and extrinsic (redshift, sky location, inclination angle, etc.) GW parameters from initialized priors - Calculates the probability of detection (Pdet) for each event based on detector network sensitivity - Stores the output in ./ler_data/gw_param.json
Parameters: - size: Total number of events to sample - batch_size: Events per batch (useful for resuming interrupted simulations) - resume: If True (default), resume from last saved batch; if False, start fresh - save_batch: If True, save after each batch; if False (default), save only at the end
Note: For realistic results, use size >= 1,000,000 with batch_size = 100,000
[36]:
# Simulate 100,000 GW events in batches of 50,000
gw_param_all = ler.gw_cbc_statistics(100000, resume=False)
# # with all input args
# gw_param_all = ler.gw_cbc_statistics(size=100000, batch_size=50000, resume=True, save_batch=False, output_jsonfile='gw_param.json')
print(f"\nTotal events simulated: {len(gw_param_all['zs'])}")
print(f"Sampled redshift values: {gw_param_all['zs'][:5]}")
Simulated GW params will be stored in ./ler_data/gw_param.json
Batch no. 1
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
Batch no. 2
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
saving all gw parameters in ./ler_data/gw_param.json
Total events simulated: 100000
Sampled redshift values: [1.79134769 3.81532071 6.88004063 0.94640131 0.64046894]
1.3 Calculate Detection Rates
Select detectable events and calculate the detection rate. This function: - Filters events using a Pdet threshold. By default, Pdet is based on observed SNR > 10, where the observed SNR follows a non-central chi-squared distribution centered at the optimal SNR. - Returns the rate in detectable events per year. - Saves detectable events to ./ler_data/gw_param_detectable.json.
[42]:
# Calculate the detection rate and extract detectable events
detectable_rate, gw_param_detectable = ler.gw_rate()
print(f"\n=== Detection Rate Summary ===")
print(f"Detectable event rate: {detectable_rate:.2e} events per year")
print(f"Total event rate: {ler.normalization_pdf_z:.2e} events per year")
print(f"Percentage fraction of the detectable events: {detectable_rate/ler.normalization_pdf_z*100:.2e}%")
Getting gw parameters from json file ./ler_data/gw_param.json...
total GW event rate (yr^-1): 270.52624492169423
number of simulated GW detectable events: 329
number of simulated all GW events: 100000
storing detectable params in ./ler_data/gw_param_detectable.json
=== Detection Rate Summary ===
Detectable event rate: 2.71e+02 events per year
Total event rate: 8.22e+04 events per year
Percentage fraction of the detectable events: 3.29e-01%
1.4 Inspect Generated Parameters
View the available parameters in the generated event population.
[43]:
# List all parameters saved for detectable events
print("Detectable event parameters:")
print(list(gw_param_detectable.keys()))
print("\nExample values for mass_1_source (detector frame):")
print(gw_param_detectable['mass_1_source'][:5])
Detectable event parameters:
['zs', 'geocent_time', 'ra', 'dec', 'phase', 'psi', 'theta_jn', 'a_1', 'a_2', 'luminosity_distance', 'mass_1_source', 'mass_2_source', 'mass_1', 'mass_2', 'pdet_L1', 'pdet_H1', 'pdet_V1', 'pdet_net']
Example values for mass_1_source (detector frame):
[27.80174506 13.5874931 26.44581764 15.18232487 11.86442242]
1.5 Access Saved Data Files
All simulation results are saved in JSON files for future reference and analysis.
[44]:
# View the directory structure and file names
print(f"Output directory: {ler.ler_directory}")
print(f"\nSaved JSON files:")
for key, filename in ler.json_file_names.items():
print(f" {key}: {filename}")
Output directory: ./ler_data
Saved JSON files:
gwrates_params: gwrates_params.json
gw_param: gw_param.json
gw_param_detectable: gw_param_detectable.json
1.6 Load and Examine Saved Parameters
Reload parameters from JSON files for further analysis.
[45]:
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json, load_json
# Load detectable parameters from file
gw_param_from_file = get_param_from_json(
ler.ler_directory + '/' + ler.json_file_names['gw_param_detectable']
)
print(f"Parameters loaded from file: {list(gw_param_from_file.keys())}")
# Load the initialization parameters and rates
gwrates_params = load_json(ler.ler_directory + '/gwrates_params.json')
print(f"\nDetectable event rate (from saved file): {gwrates_params['detectable_gw_rate_per_year']:.4e} per year")
Parameters loaded from file: ['zs', 'geocent_time', 'ra', 'dec', 'phase', 'psi', 'theta_jn', 'a_1', 'a_2', 'luminosity_distance', 'mass_1_source', 'mass_2_source', 'mass_1', 'mass_2', 'pdet_L1', 'pdet_H1', 'pdet_V1', 'pdet_net']
Detectable event rate (from saved file): 2.7053e+02 per year
1.7 Examine Available Prior Functions
View the built-in GW parameter sampler functions and their default parameters.
[48]:
# Display all available GW prior sampler functions
print("Built-in GW parameter sampler functions and parameters:\n")
for func_name, func_params in ler.available_gw_prior.items():
print(f"{func_name}:")
if isinstance(func_params, dict):
for param_name, param_value in func_params.items():
print(f" {param_name}: {param_value}")
else:
print(f" {func_params}")
print()
Built-in GW parameter sampler functions and parameters:
merger_rate_density:
merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018: {'R0': 2.39e-08, 'b2': 1.6, 'b3': 2.1, 'b4': 30}
sfr_madau_fragos2017: {'a': 0.01, 'b': 2.6, 'c': 3.2, 'd': 6.2}
sfr_madau_dickinson2014: {'a': 0.015, 'b': 2.7, 'c': 2.9, 'd': 5.6}
sfr_with_time_delay: {'R0': 2.39e-08, 'a': 0.01, 'b': 2.6, 'c': 3.2, 'd': 6.2, 'td_min': 0.01, 'td_max': 10.0}
merger_rate_density_bbh_popIII_ken2022: {'n0': 1.92e-08, 'aIII': 0.66, 'bIII': 0.3, 'zIII': 11.6}
merger_rate_density_bbh_primordial_ken2022: {'n0': 4.4e-11, 't0': 13.786885302009708}
sfr_madau_fragos2017_with_bbh_dt: {'R0': 2.39e-08}
sfr_madau_dickinson2014_with_bbh_dt: {'R0': 2.39e-08}
sfr_madau_fragos2017_with_bns_dt: {'R0': 1.0550000000000001e-07}
sfr_madau_dickinson2014_with_bns_dt: {'R0': 1.0550000000000001e-07}
zs:
source_redshift: None
source_frame_masses:
binary_masses_BBH_popI_II_powerlaw_gaussian: {'mminbh': 4.98, 'mmaxbh': 112.5, 'alpha': 3.78, 'mu_g': 32.27, 'sigma_g': 3.88, 'lambda_peak': 0.03, 'delta_m': 4.8, 'beta': 0.81}
binary_masses_BBH_popIII_lognormal: {'m_min': 5.0, 'm_max': 150.0, 'Mc': 30.0, 'sigma': 0.3}
binary_masses_BBH_primordial_lognormal: {'m_min': 1.0, 'm_max': 100.0, 'Mc': 20.0, 'sigma': 0.3}
binary_masses_NSBH_broken_powerlaw: {'mminbh': 26, 'mmaxbh': 125, 'alpha_1': 6.75, 'alpha_2': 6.75, 'b': 0.5, 'delta_m': 5, 'mminns': 1.0, 'mmaxns': 3.0, 'alphans': 0.0}
binary_masses_uniform: {'m_min': 1.0, 'm_max': 3.0}
binary_masses_BNS_bimodal: {'w': 0.643, 'muL': 1.352, 'sigmaL': 0.08, 'muR': 1.88, 'sigmaR': 0.3, 'mmin': 1.0, 'mmax': 2.3}
a_1:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8}
a_2:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': -0.8, 'xmax': 0.8}
tilt_1:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_sine: None
tilt_2:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_sine: None
phi_12:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586}
phi_jl:
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586}
geocent_time:
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 1238166018, 'xmax': 1269723618.0}
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 1238166018}
ra:
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586}
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
dec:
sampler_cosine: None
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': -1.5707963267948966, 'xmax': 1.5707963267948966}
phase:
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586}
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
psi:
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 3.141592653589793}
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
theta_jn:
sampler_sine: None
constant_values_n_size: {'value': 0.0}
sampler_uniform: {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 3.141592653589793}
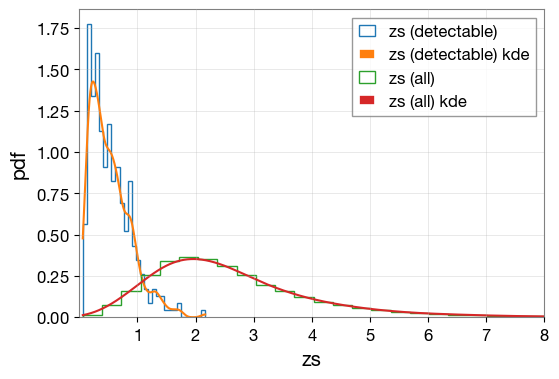
1.8 Visualize Parameter Distributions
Create KDE (Kernel Density Estimation) plots to compare the distributions of parameters between all simulated events and detectable events.
[49]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ler.utils import plots as lerplt
# input param_dict can be either a dictionary or a json file name that contains the parameters
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
lerplt.param_plot(
param_name='zs',
param_dict='ler_data/gw_param_detectable.json',
plot_label='zs (detectable)',
)
lerplt.param_plot(
param_name='zs',
param_dict='ler_data/gw_param.json',
plot_label='zs (all)',
)
plt.xlim(0.001,8)
plt.xlabel('zs')
plt.ylabel('pdf')
plt.grid(alpha=0.4)
plt.show()
getting gw_params from json file ler_data/gw_param_detectable.json...
getting gw_params from json file ler_data/gw_param.json...
Part 2: Custom Functions and Parameters
This section demonstrates how to customize GWRATES with your own sampling functions and detection criteria. We’ll create a BNS (Binary Neutron Star) example with custom settings:
Component |
Custom Configuration |
Default (BBH) |
|---|---|---|
Event Type |
BNS (non-spinning) |
BBH (spinning, aligned) |
Merger Rate |
Madau-Dickinson (2014) |
GWTC-4 based |
Source Masses |
Uniform 1.0-2.3 \(M_{\odot}\) |
Bimodal Gaussian |
Detectors |
3G (ET, CE), SNR > 12 |
O4 (H1, L1, V1), SNR > 10 |
Notes: - GW parameter sampling priors: Should be a function with size as the only input argument. Can also be a class object of ler.utils.FunctionConditioning. - Merger rate density: Should be a function of F(z).
2.2 Define Event Type with Non-Spinning Configuration
Using event_type='BNS' in the LeR class initialization will default to the following GW parameter priors corresponding to BNS. Other allowed event types are ‘BBH’ and ‘NSBH’.
source_priors = dict(
merger_rate_density = 'merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson2014',
source_frame_masses = 'binary_masses_BNS_bimodal',
a_1 = 'sampler_uniform',
a_2 = 'sampler_uniform',
),
source_priors_params= dict(
merger_rate_density = dict(
R0=89 * 1e-9,
a=0.015,
b=2.7,
c=2.9,
d=5.6,
),
source_frame_masses = dict(
w=0.643,
muL=1.352,
sigmaL=0.08,
muR=1.88,
sigmaR=0.3,
mmin=1.0,
mmax=2.3,
),
a_1 = dict(xmin=-0.05, xmax=0.05),
a_2 = dict(xmin=-0.05, xmax=0.05),
),
We will change some of these priors with our custom ones in the next sections.
For non-spinning configuration (faster calculation in our example), we can set:
spin_zero=True,
spin_precession=False,
2.2 Define Custom Merger Rate Density
Using the default BNS merger rate density prior model, we change the local merger rate density from the default value of \(R_0 = 89 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{Mpc}^{-3}\text{yr}^{-1}\) (GWTC-4) to \(R_0 = 105.5 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{Mpc}^{-3}\text{yr}^{-1}\) (GWTC-3).
2.3 Define Custom Merger Rate Density
Using the default BNS merger rate density prior model, we change the local merger rate density from the default value of \(R_0 = 89 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{Mpc}^{-3}\text{yr}^{-1}\) (GWTC-4) to \(R_0 = 105.5 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{Mpc}^{-3}\text{yr}^{-1}\) (GWTC-3).
[ ]:
# Use built-in Madau-Dickinson (2014) SFR based merger rate density for BNS
merger_rate_density_function = 'merger_rate_density_madau_dickinson2014'
# Custom parameters for merger rate density (Madau-Dickinson model)
merger_rate_density_input_args = dict(
R0=89e-9, # Local merger rate density (Mpc^-3 yr^-1)
a=0.015, # Evolution parameter a
b=2.7, # Evolution parameter b
c=2.9, # Evolution parameter c
d=5.6, # Evolution parameter d
)
print("Merger rate density function:", merger_rate_density_function)
print("Parameters:", merger_rate_density_input_args)
Merger rate density function: merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018
Parameters: {'R0': 1.0550000000000001e-07, 'b2': 1.6, 'b3': 2.1, 'b4': 30}
2.1 Define Custom Source Frame Masses
Use a uniform distribution to sample binary masses (mass_1 and mass_2). Ensure mass_1 >= mass_2 by swapping if necessary.
[ ]:
import numpy as np
# Define mass range for BNS
source_frame_masses_args = dict(
mmin=1.0, # Minimum mass in solar masses
mmax=2.3, # Maximum mass in solar masses
)
def source_frame_masses_uniform(size, mmin=source_frame_masses_args['mmin'], mmax=source_frame_masses_args['mmax']):
"""
Sample mass_1 and mass_2 uniformly from a specified range, ensuring mass_1 >= mass_2 by swapping if necessary.
Parameters
----------
size : int
Number of samples to draw
mmin : float, optional
Minimum mass in solar masses (default: 1.0)
mmax : float, optional
Maximum mass in solar masses (default: 2.3)
Returns
-------
mass_1_source : ndarray
Array of primary mass samples (larger mass)
mass_2_source : ndarray
Array of secondary mass samples (smaller mass)
"""
# Sample masses uniformly
mass_1_source = np.random.uniform(mmin, mmax, size)
mass_2_source = np.random.uniform(mmin, mmax, size)
# Ensure mass_1 >= mass_2 by swapping if necessary
idx = mass_2_source > mass_1_source
mass_1_source[idx], mass_2_source[idx] = mass_2_source[idx], mass_1_source[idx]
return (mass_1_source, mass_2_source)
# Test the function
m1_test, m2_test = source_frame_masses_uniform(size=5)
print("Test mass samples:")
print(f" mass_1: {m1_test}")
print(f" mass_2: {m2_test}")
print(f" mass_1 >= mass_2: {(m1_test >= m2_test).all()}")
Test mass samples:
mass_1: [1.25390248 1.97542099 1.824485 2.15927396 1.63832471]
mass_2: [1.04427987 1.2296851 1.01247127 1.54740765 1.0178791 ]
mass_1 >= mass_2: True
2.4 Define Custom Detection Criteria
Create a custom detection function using 3G detectors (Einstein Telescope and Cosmic Explorer) with a higher SNR threshold. We use pdet = optimal_SNR_net > 12 instead of the default pdet based on observed_SNR_net > 10.
This function takes GW parameters as input and returns Pdet as a boolean or probability array indicating detectability.
[ ]:
from gwsnr import GWSNR
# Define mass and redshift ranges for BNS
mmin = 1.0
mmax = 2.3
zmin = 0.0
zmax = 10.0
snr_threshold_network = 12 # SNR threshold for detection (default: 10)
# Initialize GWSNR for 3G detectors (no spins for BNS)
gwsnr_3g = GWSNR(
npool=4,
ifos=['ET', 'CE'], # Einstein Telescope and Cosmic Explorer
snr_method='interpolation_no_spins', # No spin precession for BNS
mtot_min=2*mmin*(1+zmin),
mtot_max=2*mmax*(1+zmax),
sampling_frequency=2048.0,
waveform_approximant='IMRPhenomD',
minimum_frequency=20.0,
gwsnr_verbose=False,
)
def detection_criteria(gw_param_dict):
"""
Determine if a gravitational wave event is detectable based on SNR threshold.
Parameters
----------
gw_param_dict : dict
Dictionary containing GW parameters including mass_1, mass_2, luminosity_distance, etc.
Returns
-------
dict
Dictionary with 'pdet_net' (boolean detection array) and 'optimal_snr_net'
"""
result_dict = {}
# Calculate optimal SNR for all detectors
snr_dict = gwsnr_3g.optimal_snr(gw_param_dict=gw_param_dict)
# Apply detection threshold
result_dict['pdet_net'] = snr_dict['optimal_snr_net'] > snr_threshold_network
return result_dict
print("Custom detection criteria defined for 3G detectors (ET + CE)")
print(f"Detection network SNR threshold: {snr_threshold_network}")
# Test the detection criteria function
gw_param_dict = dict(
mass_1 = np.array([2.0, 2.0]),
mass_2 = np.array([1.0, 1.0]),
luminosity_distance = np.array([1000.0, 10000.0]),
)
pdet = detection_criteria(gw_param_dict=gw_param_dict)
print("\nTest detection calculation:")
print(f" mass_1 array: {gw_param_dict['mass_1']}")
print(f" mass_2 array: {gw_param_dict['mass_2']}")
print(f" luminosity_distance array: {gw_param_dict['luminosity_distance']}")
print(f" Pdet result: {pdet}")
Initializing GWSNR class...
Interpolator will be loaded for ET1 detector from ./interpolator_json/ET1/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for ET2 detector from ./interpolator_json/ET2/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for ET3 detector from ./interpolator_json/ET3/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Interpolator will be loaded for CE detector from ./interpolator_json/CE/partialSNR_dict_0.json
Custom detection criteria defined for 3G detectors (ET + CE)
Detection network threshold: 12 SNR
Test Pdet calculation:
mass_1 array : [2. 2.]
mass_2 array : [1. 1.]
luminosity_distance array: [ 1000. 10000.]
Pdet array : {'pdet_net': array([ True, False])}
2.5 Initialize GWRATES with Custom Settings
Create a GWRATES instance with the custom functions and parameters defined above.
[ ]:
from ler import GWRATES
# Initialize GWRATES with custom functions
ler_custom = GWRATES(
# LeR setup parameters
npool=6,
z_min=0.001,
z_max=10,
verbose=True,
event_type="BNS", # Binary Neutron Star
spin_zero=True,
# Custom source parameter priors
source_priors=dict(
merger_rate_density=merger_rate_density_function,
source_frame_masses=source_frame_masses_uniform, # Custom function
),
source_priors_params=dict(
merger_rate_density=merger_rate_density_input_args,
source_frame_masses=source_frame_masses_args,
),
# Custom detection criteria
pdet_finder=detection_criteria,
ler_directory='./ler_data_custom', # Save in a separate directory
)
Initializing GWRATES class...
Initializing CBCSourceRedshiftDistribution...
luminosity_distance interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/luminosity_distance/luminosity_distance_2.json
differential_comoving_volume interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/differential_comoving_volume/differential_comoving_volume_2.json
using ler available merger rate density model: merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018
merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018 interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018_4.json
merger_rate_density_detector_frame interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/merger_rate_density/merger_rate_density_detector_frame_5.json
source_redshift interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/source_redshift/source_redshift_2.json
Initializing CBCSourceParameterDistribution...
using ler available zs function : source_redshift
using user defined custom source_frame_masses function
using ler available geocent_time function : sampler_uniform
using ler available ra function : sampler_uniform
using ler available dec function : sampler_cosine
using ler available phase function : sampler_uniform
using ler available psi function : sampler_uniform
using ler available theta_jn function : sampler_sine
using ler available a_1 function : sampler_uniform
using ler available a_2 function : sampler_uniform
#----------------------------------------
# GWRATES initialization input arguments:
#----------------------------------------
# GWRATES set up input arguments:
npool = 4,
z_min = 0.001,
z_max = 10,
event_type = 'BNS',
cosmology = LambdaCDM(H0=70.0 km / (Mpc s), Om0=0.3, Ode0=0.7, Tcmb0=0.0 K, Neff=3.04, m_nu=None, Ob0=None),
pdet_finder = <function detection_criteria at 0x30282aa70>,
json_file_names = dict(
gwrates_params = 'gwrates_params.json',
gw_param = 'gw_param.json',
gw_param_detectable = 'gw_param_detectable.json',
),
interpolator_directory = './interpolator_json',
ler_directory = './ler_data_custom',
# GWRATES also takes other CBCSourceParameterDistribution class input arguments as kwargs, as follows:
source_priors = dict(
merger_rate_density = 'merger_rate_density_bbh_oguri2018',
zs = 'source_redshift',
source_frame_masses = <function source_frame_masses_uniform at 0x10af6a8c0>,
geocent_time = 'sampler_uniform',
ra = 'sampler_uniform',
dec = 'sampler_cosine',
phase = 'sampler_uniform',
psi = 'sampler_uniform',
theta_jn = 'sampler_sine',
a_1 = 'sampler_uniform',
a_2 = 'sampler_uniform',
),
source_priors_params = dict(
merger_rate_density = {'R0': 1.0550000000000001e-07, 'b2': 1.6, 'b3': 2.1, 'b4': 30},
zs = None,
source_frame_masses = {'mmin': 1.0, 'mmax': 2.3},
geocent_time = {'xmin': 1238166018, 'xmax': 1269702018},
ra = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
dec = None,
phase = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 6.283185307179586},
psi = {'xmin': 0.0, 'xmax': 3.141592653589793},
theta_jn = None,
a_1 = {'xmin': -0.05, 'xmax': 0.05},
a_2 = {'xmin': -0.05, 'xmax': 0.05},
),
spin_zero = False,
spin_precession = False,
2.6 Sample GW Parameters with Custom Settings
[23]:
# Sample GW population with custom settings
gw_params_custom = ler_custom.gw_cbc_statistics(
size=100000,
batch_size=50000,
resume=False, # Start fresh
output_jsonfile='custom_gw_params.json'
)
print(f"\nSampled {len(gw_params_custom['zs'])} custom BNS events")
Simulated GW params will be stored in ./ler_data_custom/custom_gw_params.json
Batch no. 1
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
Batch no. 2
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
saving all gw parameters in ./ler_data_custom/custom_gw_params.json
Sampled 100000 custom BNS events
2.7 Calculate Rates with Custom Settings
[ ]:
# Calculate detection rates with custom settings
detectable_rate_custom, gw_param_detectable_custom = ler_custom.gw_rate()
# Calculate fraction of detectable events
total_rate_custom = ler_custom.normalization_pdf_z
fraction_detectable = detectable_rate_custom / total_rate_custom
print(f"\n=== Custom BNS Detection Results (3G Detectors Sensitivity) ===")
print(f"Detectable BNS event rate: {detectable_rate_custom:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Total BNS event rate: {total_rate_custom:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Detectable fraction: {fraction_detectable*100:.2f}%")
Getting gw parameters from json file ./ler_data_custom/custom_gw_params.json...
total GW event rate (yr^-1): 73925.64600292277
number of simulated GW detectable events: 20367
number of simulated all GW events: 100000
storing detectable params in ./ler_data_custom/gw_param_detectable.json
=== Custom BNS Detection Results (under 3G detectors sesitivity) ===
Detectable BNS event rate: 7.3926e+04 events per year
Total BNS event rate: 3.6297e+05 events per year
Detectable fraction: 20.37%
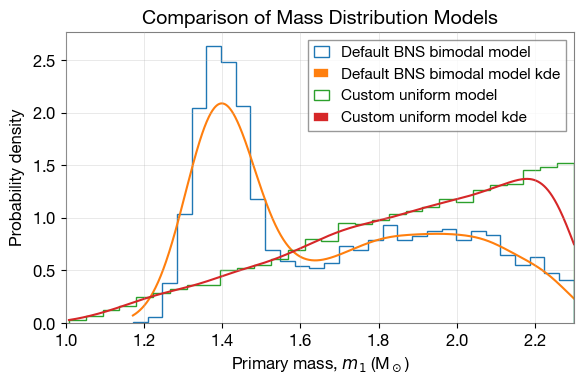
2.8 Compare Default and Custom Mass Distributions
GWRATES uses binary_masses_BNS_bimodal as the default mass distribution for BNS events. Here we compare the default distribution with our custom uniform mass distribution defined earlier.
[28]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ler.utils import plots as lerplt
# Sample from default BNS mass distribution
mass_1_default, mass_2_default = ler_custom.binary_masses_BNS_bimodal(size=10000)
default_mass_dict = dict(mass_1_source=mass_1_default)
# Sample from custom mass distribution
mass_1_custom, mass_2_custom = source_frame_masses_uniform(size=10000)
custom_mass_dict = dict(mass_1_source=mass_1_custom)
# Create comparison plot
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
# Plot default model
lerplt.param_plot(
param_name='mass_1_source',
param_dict=default_mass_dict,
plot_label='Default BNS bimodal model',
)
# Plot custom model
lerplt.param_plot(
param_name='mass_1_source',
param_dict=custom_mass_dict,
plot_label='Custom uniform model',
)
plt.xlabel(r'Primary mass, $m_1$ (M$_\odot$)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Probability density', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Comparison of Mass Distribution Models', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlim(1, 2.3)
plt.legend(fontsize=11)
plt.grid(alpha=0.4)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
binary_masses_BNS_bimodal interpolator will be loaded from ./interpolator_json/source_frame_masses/binary_masses_BNS_bimodal_0.json
Part 3: Advanced Sampling - Generating Detectable Events
This section demonstrates how to generate a specific number of detectable events and monitor detection rate convergence.
3.1 Initialize GWRATES for N-Event Sampling
[29]:
# Create a new GWRATES instance for N-event sampling
ler_n_events = GWRATES(
npool=6,
verbose=False,
)
Initializing GWRATES class...
3.2 Sample Until N Detectable Events Are Found
This function will: - Continue sampling in batches until at least N detectable events are found - Monitor rate convergence using a stopping criteria (e.g., relative rate difference < 0.5%) - Calculate rates dynamically at each batch - Allow resuming from the last batch if interrupted
[ ]:
# Sample until we have at least 10,000 detectable events with converged rates
detectable_rate_n, gw_param_detectable_n = ler_n_events.selecting_n_gw_detectable_events(
size=10000, # Target number of detectable events
batch_size=100000, # Events per batch
stopping_criteria=dict(
relative_diff_percentage=0.5, # Stop when rate change < 0.5% (use 0.1% for better convergence)
number_of_last_batches_to_check=4 # Check last 4 batches
),
pdet_threshold=0.5, # Probability threshold for detection
resume=False, # Start fresh
output_jsonfile='gw_params_n_detectable.json',
meta_data_file='meta_gw.json', # Store metadata (rates per batch)
pdet_type='boolean',
trim_to_size=False, # Keep all events found until convergence
)
print(f"\n=== N-Event Sampling Results ===")
print(f"Detectable event rate: {detectable_rate_n:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Collected number of detectable events: {len(gw_param_detectable_n['zs'])}")
stopping criteria set to when relative difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches is less than 0.5%.
sample collection will stop when the stopping criteria is met and number of detectable events exceeds the specified size.
removing ./ler_data/gw_params_n_detectable.json and ./ler_data/meta_gw.json if they exist
collected number of detectable events = 0
collected number of detectable events = 334
total number of events = 100000
total rate (yr^-1): 274.6375860299267
collected number of detectable events = 656
total number of events = 200000
total rate (yr^-1): 269.7039767000478
collected number of detectable events = 948
total number of events = 300000
total rate (yr^-1): 259.8367580402899
collected number of detectable events = 1287
total number of events = 400000
total rate (yr^-1): 264.56480031475724
collected number of detectable events = 1657
total number of events = 500000
total rate (yr^-1): 272.4996886536458
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [1.02595051 4.64695232 2.91188896 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 2016
total number of events = 600000
total rate (yr^-1): 276.28212247321966
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [5.95238095 4.24107143 1.36904762 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 2369
total number of events = 700000
total rate (yr^-1): 278.2790595829326
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [4.92823976 2.07682566 0.71760236 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 2725
total number of events = 800000
total rate (yr^-1): 280.08511299833464
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [2.70825688 1.35779817 0.64482307 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 3108
total number of events = 900000
total rate (yr^-1): 283.95662587525356
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [2.7027027 1.99944843 1.36341699 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 3472
total number of events = 1000000
total rate (yr^-1): 285.4915265556603
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [2.52633311 1.8937212 0.53763441 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 3862
total number of events = 1100000
total rate (yr^-1): 288.6908974544303
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [2.98096841 1.63991024 1.10823408 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 4175
total number of events = 1200000
total rate (yr^-1): 286.0808187811736
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.74251497 0.20598802 0.9123571 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 4505
total number of events = 1300000
total rate (yr^-1): 284.94756450134037
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.190899 1.31369186 0.39770625 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 4849
total number of events = 1400000
total rate (yr^-1): 284.79847191170114
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [1.36672978 0.45026466 0.05235021 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 5170
total number of events = 1500000
total rate (yr^-1): 283.40844706082254
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.94294004 0.54307395 0.49046698 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 5540
total number of events = 1600000
total rate (yr^-1): 284.71037174509615
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.08331019 0.03094379 0.45728039 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 5883
total number of events = 1700000
total rate (yr^-1): 284.5531734086049
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.0862048 0.40228908 0.05524392 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 6224
total number of events = 1800000
total rate (yr^-1): 284.3220784182075
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.32133676 0.13656812 0.0812793 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 6586
total number of events = 1900000
total rate (yr^-1): 285.02413198756653
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.11008199 0.16523463 0.24631373 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 6905
total number of events = 2000000
total rate (yr^-1): 283.8881035234497
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.23427184 0.15286829 0.40016769 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 7210
total number of events = 2100000
total rate (yr^-1): 282.3120894319606
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.71197411 0.96065406 0.55825243 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 7555
total number of events = 2200000
total rate (yr^-1): 282.374382479055
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.93838169 0.53606883 0.02206045 0. ]
collected number of detectable events = 7905
total number of events = 2300000
total rate (yr^-1): 282.6100127006731
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.45224541 0.10541851 0.08337646 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 8234
total number of events = 2400000
total rate (yr^-1): 282.1065223765489
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.07286859 0.09494999 0.17847525 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 8578
total number of events = 2500000
total rate (yr^-1): 282.1366722113426
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.08425359 0.16776993 0.01068625 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 8909
total number of events = 2600000
total rate (yr^-1): 281.75336871725204
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.30404037 0.12534142 0.1360422 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 9248
total number of events = 2700000
total rate (yr^-1): 281.6420931032116
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.16490052 0.17560554 0.03950958 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 9563
total number of events = 2800000
total rate (yr^-1): 280.833964414477
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.46387117 0.32738359 0.28776031 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 9906
total number of events = 2900000
total rate (yr^-1): 280.87548288379656
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.31255339 0.27293597 0.01478181 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
collected number of detectable events = 10244
total number of events = 3000000
total rate (yr^-1): 280.77718875155375
percentage difference of total rate for the last 4 cumulative batches = [0.30803939 0.0202209 0.03500788 0. ]
stopping criteria of rate relative difference of 0.5% for the last 4 cumulative batches reached.
Given size=10000 reached
stored detectable GW params in ./ler_data/gw_params_n_detectable.json
stored meta data in ./ler_data/meta_gw.json
=== N-Event Sampling Results ===
Detectable event rate: 2.8078e+02 events per year
Collected number of detectable events: 10244
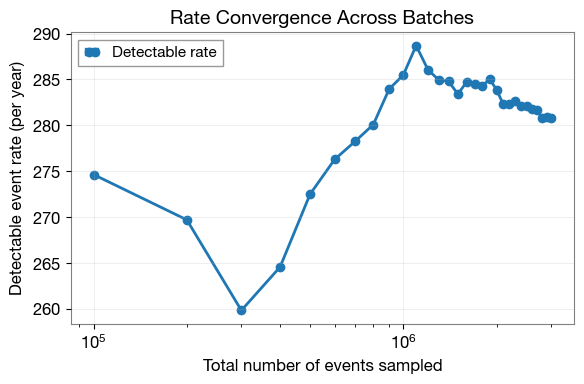
3.3 Analyze Rate Convergence
Plot the evolution of the detection rate across batches to verify convergence.
[47]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
# Load metadata containing rates for each batch
meta_data = get_param_from_json(ler_n_events.ler_directory + '/meta_gw.json')
# Plot rate vs sampling size
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(
meta_data['events_total'],
meta_data['total_rate'],
'o-',
linewidth=2,
markersize=6,
label='Detectable rate'
)
plt.xlabel('Total number of events sampled', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Detectable event rate (per year)', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Rate Convergence Across Batches', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend(fontsize=11)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3.4 Assess Rate Stability
Calculate the average rate from the last batches to verify convergence.
[ ]:
import numpy as np
# Select rates from the last batches
idx_converged = [-4, -3, -2, -1]
rates_converged = np.array(meta_data['total_rate'])[idx_converged]
if len(rates_converged) > 0:
mean_rate = rates_converged.mean()
std_rate = rates_converged.std()
print(f"\n=== Rate Stability Analysis ===")
print(f"Number of converged batches: {len(rates_converged)}")
print(f"Mean rate (converged): {mean_rate:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Standard deviation: {std_rate:.4e} events per year")
print(f"Relative uncertainty: {(std_rate/mean_rate)*100:.2f}%")
else:
print("Not enough batches to assess convergence.")
=== Rate Stability Analysis ===
Number of converged batches: 4
Mean rate (converged): 2.8103e+02 events per year
Standard deviation: 3.5386e-01 events per year
Relative uncertainty: 0.13%
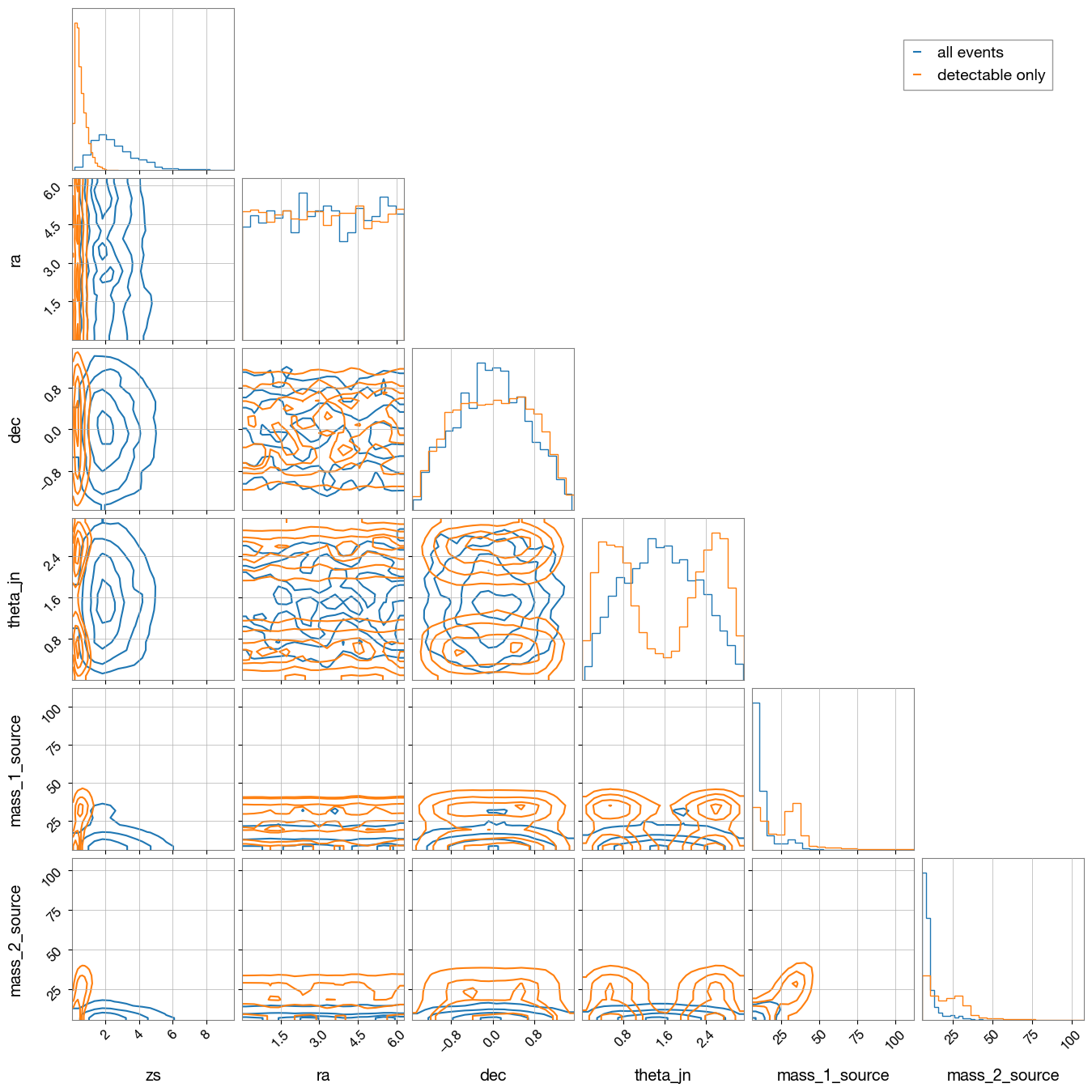
3.5 Compare All Sampled and Detectable Event Parameters
Create an overlapping visualization comparing the parameter distributions of all sampled events with detectable events only.
[49]:
# generate CBC (all) parameters
gw_param = ler_n_events.gw_cbc_statistics(10000, resume=False)
Simulated GW params will be stored in ./ler_data/gw_param.json
Batch no. 1
sampling gw source params...
calculating pdet...
gw parameters already sampled.
[ ]:
import corner
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
from ler.utils import get_param_from_json
param = get_param_from_json('ler_data/gw_param.json')
param_detectable = get_param_from_json('./ler_data/gw_params_n_detectable.json')
param_names = ['zs', 'ra', 'dec', 'theta_jn', 'mass_1_source', 'mass_2_source']
# Prepare data for corner plot
samples_unlensed = np.stack([param[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
samples_detectable = np.stack([param_detectable[p] for p in param_names], axis=1)
# Generate corner plot
fig = corner.corner(
samples_unlensed,
labels=param_names,
color='C0',
alpha=0.5,
plot_density=False, plot_datapoints=False, smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
blue_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C0', label='all events')
# Plot detectable events
corner.corner(
samples_detectable,
labels=param_names,
color='C1',
alpha=0.5,
fig=fig,
plot_density=False, plot_datapoints=False, smooth=0.8,
hist_kwargs={'density': True}
)
orange_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='C1', label='detectable only')
# Add legend
fig.legend(handles=[blue_line, orange_line], loc='upper right', bbox_to_anchor=(0.95, 0.95), fontsize=14)
plt.show()
WARNING:root:Too few points to create valid contours
Summary
This notebook demonstrated the key features of the GWRATES class:
Basic Simulation: Simulating GW populations and calculating detection rates
Customization: Using custom mass distributions, merger rate densities, and detection criteria
Advanced Sampling: Generating a specific number of detectable events and monitoring rate convergence
Visualization: Comparing distributions and analyzing results
For more examples and detailed documentation, visit the ler documentation.
Key Takeaways: - GWRATES is flexible and supports custom prior functions - Batching allows resumable simulations and memory-efficient sampling - Rate convergence can be monitored and validated - Results are automatically saved for reproducibility and further analysis
